
论文题目:Super-Hydrophilic/Aerophobic Co(OH)2/NiFe Layered Double Hydroxide Heterostructures with Moderate Work Function Difference for Large-Current-Density Electrochemical Ammonia Synthesis
论文作者:Yi Feng, Jin-Tao Ren, Yue-Xin Song, Wen-Wen Tian, Hao-Yu, Wang, Lei Wang, Ming-Lei Sun and Zhong-Yong Yuan*
发表期刊:CCS Chem
Abstract
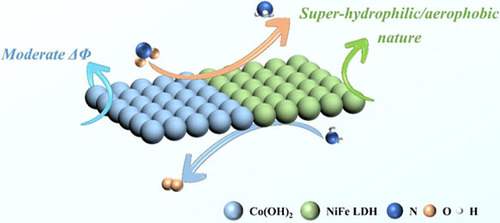
Developing NO2− reduction reaction (NO2−RR) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER) bifunctional electrocatalysts at large current densities is crucial for decreasing energy consumption of electrocatalytic NH3 production and booming sustainable nitrogen-based economy. In addition to increasing active sites of catalysts, bubble adhesion deserves more attention during high-current electrolysis, which can deteriorate mass transfer and block active sites in gas-involving environments. Herein, super-hydrophilic/aerophobic cobalt-nickel-iron layered double hydroxide [Co(OH)2/NiFe LDH] core-shell heterostructures were developed as efficient NO2−RR and OER electrocatalysts to optimize surface tension due to self-pumping effect and modify active hydrogen adsorption behavior owing to moderate work function difference between Co(OH)2 and NiFe LDH. The fabricated Co(OH)2/NiFe LDH exhibited excellent NO2−RR activity (yield: 50 mg h−1 cm−2; FE: 91% at −500 mA cm−2) and impressive OER behavior (η1000: 340 mV) accompanied by remarkable application potential for renewable energy-driven two-electrode system to produce NH3. This effort revealed important insights into the development of electrodes for reaching cost-effective electrocatalytic ammonia production at large current densities.
