
论文题目:Modulating interfacial charge diatribution of Ni2P-NiSe2 by multiple ineterface engineering for accelerating water splitting with industry-level activity and stability
论文作者:Jin-Tao Ren, Lei Chen, Hao-Yu Wang, Wen-Wen Tian, Si-Xiang Zhai, Yi Feng, Zhong-Yong Yuan*
发表期刊:10.1016/j.apcatb.2024.123817
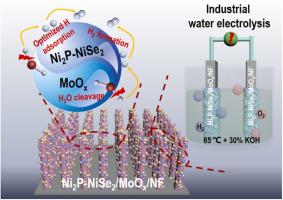
Abstract
Suitable electrocatalysts for industrial water splitting can veritably promote practical hydrogen applications. Guided by density functional theory calculations, the interface-rich NiP-NiSe nanoparticles anchored on amorphous MoO nanorods on nickel foam (NiP-NiSe/MoO/NF) are fabricated. NiP-NiSe/MoO/NF exhibits exceptional HER performance with overpotentials of 23 and 263 mV at 10 and 500 mA cm, outperforming most reported non-Pt based electrocatalysts reported hitherto. Remarkably, the excellent oxygen evolution activity (241 mV at 10 mA cm) of NiP-NiSe/MoO/NF further realizes the full electrolyzer requiring the voltage of 1.63 V at 50 mA cm with robust stability (1000 h at 20 mA cm) in 1.0 M KOH. At industrial conditions (30% KOH, 65 ℃), only 2.02 V is required to reach 1000 mA cm with satisfying durability (200 h at 200 mA cm). When deployed in anion exchange membrane water electrolyzer, the catalyst achieves 1.3 A cm at 2.7 V, associated with the prolonged stability.
