
论文题目:Synergy of Epitaxial Layer and Bulk Doping Enables Structural Rigidity of Cobalt-Free Ultrahigh-Nickel Oxide Cathode for Lithium-Ion Batteries
论文作者:Yang-Yang Wang, Zhiming Liang, Zhi-Chao Liu, Sheng Liu*, Chunmei Ban*, Guo-Ran Li, Xue-Ping Gao*
发表期刊:Adv. Funct. Mater.2023, 2308152.
Abstract
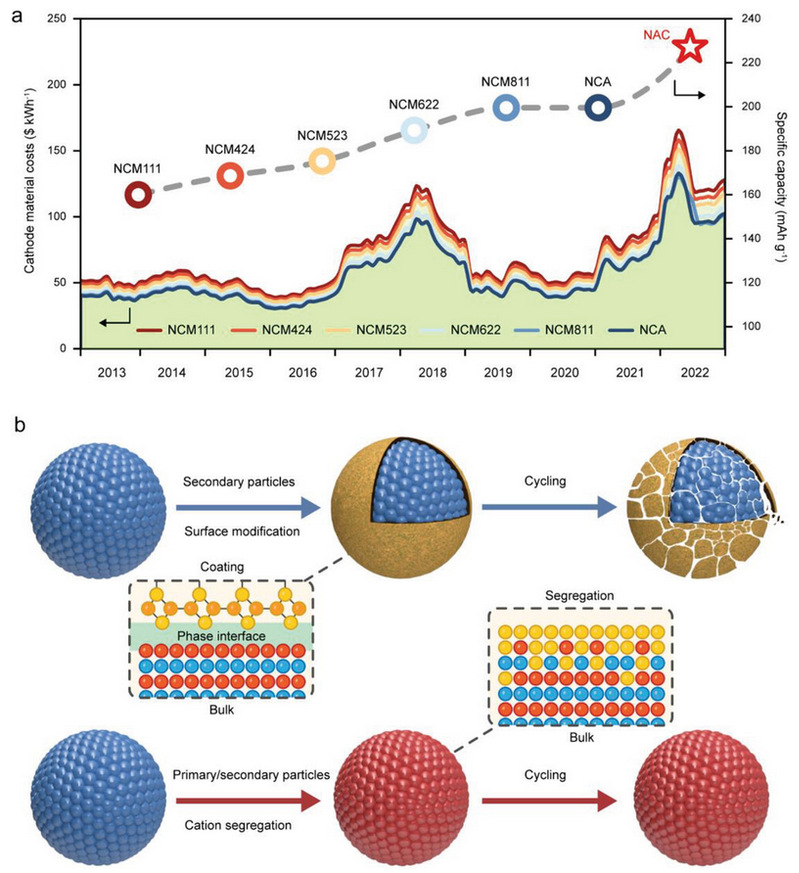
Cobalt-free ultrahigh-nickel layered oxide cathodes hold great promise for reducing the cost and enhancing the energy density of Li-ion batteries. However, the increasing Ni content and the elimination of Co could cause severe interfacial and structural degradation, leading to poor electrochemical performance of ultrahigh-nickel layered oxide cathodes. Here, a Co-free oxide, LiNi0.96Al0.03Ca0.01O2 (NAC), where Ca acts as pillar ions at the surface and Al works as an oxygen stabilizer across the bulk, is presented. An epitaxial layer rich in segregated Ca can effectively inhibit adverse surface reconstruction at high states of charge, together with the oxygen stabilization of bulk phase by doping Al, significantly reinforcing the structural rigidity of the layered oxide during cycling. The fabricated NAC cathode material exhibits exceptional electrochemical performance in terms of high cycling stability with 93% capacity retention over 500 cycles and a material-level energy density of ~800 Wh kg−1. This study provides an efficient and feasible strategy to design and stabilize ultrahigh-nickel oxides for lithium-ion batteries.
