 Title:High-entropy perovskite oxide nanofibers as efficient bidirectional electrocatalyst of liquid-solid conversion processes in lithium-sulfur batteries
Title:High-entropy perovskite oxide nanofibers as efficient bidirectional electrocatalyst of liquid-solid conversion processes in lithium-sulfur batteries
Authors:Liyuan Tian, Ze Zhang*, Sheng Liu, Guoran Li, Xueping Gao*
Publication:Nano Energy,2023,106,108037
Abstract
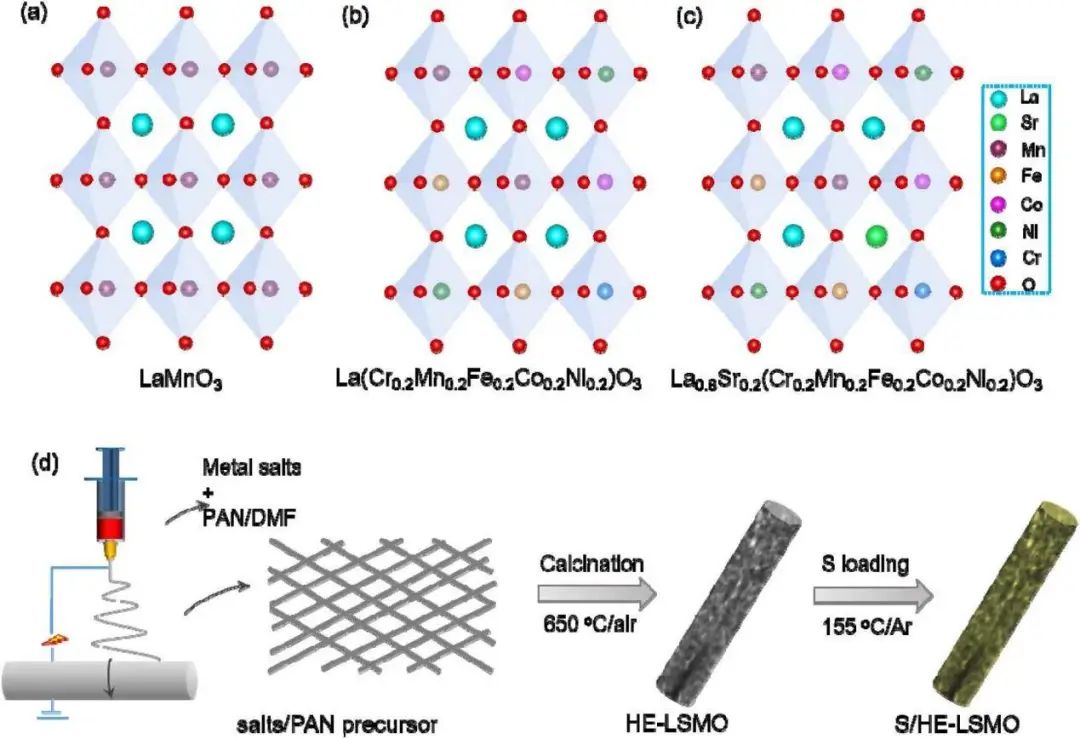
Transition metal oxides are a class of promising host materials of sulfur for lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries due to their robust polysulfide adsorption, and catalytic effect on sulfur redox reaction. It is proven that the adsorption-catalysis property can benefit a lot from incorporating multiple metal elements, and high-entropy oxides (HEOs) show good competitive potential for durable Li-S batteries. Herein, HEO nanofibers are designed as bidirectional catalytic host of sulfur to promote both the reduction of soluble intermediates and the re-oxidation of insoluble products. Specifically, the high-entropy perovskite oxide La0.8Sr0.2(Cr0.2Mn0.2Fe0.2Co0.2Ni0.2)O3 (HE-LSMO) nanofibers prepared via an electrospinning-calcination method show a unique porous fibrous structure for incorporation with sulfur. The introduced multiple metal elements can effectively modulate the binding strength of soluble polysulfides, and HE-LSMO nanofibers act as bidirectional electrocatalyst for the liquid-solid conversion processes between soluble polysulfides and insoluble Li2S, which is enabled by the high entropic contribution. As a result, the S/HE-LSMO cathode with a sulfur loading of 8.4 mg cm−2 shows a high areal capacity of 6.6 mAh cm−2 at low electrolyte/sulfur ratio of 5.3 μL mg−1, as well as good cycle stability. This work provides a foundation understanding of the bidirectional catalytic role of HEOs toward practical Li-S batteries.
 Title:High-entropy perovskite oxide nanofibers as efficient bidirectional electrocatalyst of liquid-solid conversion processes in lithium-sulfur batteries
Title:High-entropy perovskite oxide nanofibers as efficient bidirectional electrocatalyst of liquid-solid conversion processes in lithium-sulfur batteries
