
论文题目:Spectroscopic Signature of Lewis Acidic Framework and Extraframework Sn Sites in Beta Zeolites
论文作者:Weili Dai, Qifeng Lei, Guangjun Wu, Naijia Guan, Michael Hunger, Landong Li*
Abstract:
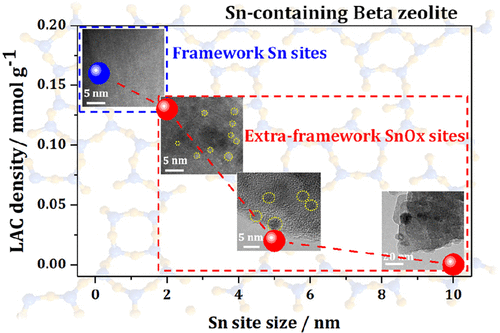
A variety of Sn-containing Beta zeolites possessing framework or extraframework Sn sites were prepared by a two-step postsynthesis procedure. The nature of these Sn species was systematically investigated by several approaches, including DRIFT, XPS, UV-vis, and solid-state Sn-119 MAS NMR spectroscopy. The subtle distinctions of the Lewis acidic features between the framework and extraframework Sn sites were identified via acetone-2-C-13, TMPO, and NH3 adsorption, studied via C-13, P-31, and H-1 MAS NMR spectroscopy, respectively. Two types of Lewis acid sites (LAS) have been observed and attributed to (i) framework Sn sites and (ii) extraframework SnOx clusters confined inside the pores or cages of [Si]Beta zeolite, both exhibiting Lewis acid properties. The Lewis acidic characteristics of the extraframework Sn sites were found to depend on the cluster sizes. The confined SnOx clusters with sizes of 0.5-2 nm possess Lewis acidic characteristics similar to those of the framework Sn species and also exhibit a comparable catalytic activity in the Baeyer-Villiger (B-V) oxidation of cyclohexanone and cyclohexene oxide hydration. With an increase in size of the SnOx clusters to over 2 nm, the Lewis acidic characteristics of the extraframework Sn species gradually weaken or even disappear.
