
论文题目:In situ encapsulated Co/MnOx nanoparticles inside quasi-MOF-74 for the higher alcohols synthesis from syngas
论文作者:Wengang Cui, Yanting Li, Hongbo Zhang, Zhengchang Wei, Bohai Gao, Jingjing Dai, Tongliang Hu*
Abstract:
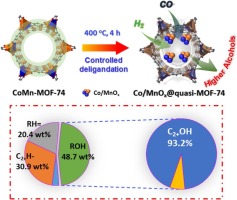
Selective conversion of syngas (CO/H-2) to higher alcohols (C2+OH) is of great interest but presents a significant challenge in keeping an appropriate balance between the carbon chain growth and CO insertion to achieve a high C2+OH selectivity. Herein we found that a core-shell Co/MnOx@quasi-MOF-74 catalyst can be easily constructed through controlled deligandation of a bimetallic CoMn-MOF-74 by partial pyrolysis strategy. The as-obtained Co/MnOx@quasi-MOF-74 catalyst produces three types of synergistic active sites (Co degrees, coordinatively unsaturated sites (CUSs) of Co2+ and Co2C) that collaborate with each other to enhance C2+OH formation during the reaction. The Co degrees nanoparticles within the framework of quasi-MOF-74 enable CO dissociation and significant CHx-CHy coupling to occur while the uniformly distributed CUSs of Co2+ working with Co2C strengthen CO insertion process, leading an outstanding catalytic performance in the process of CO hydrogenation. The total selectivity of alcohols (ROH) reached 48.7 wt%, where of 93.2 wt% can be C2+ OH, and very low CH4 and indetectable CO2 were produced at 200 degrees C, 3.0 MPa (CO/H-2 = 1/2) and a gaseous hourly space velocity (GHSV) of 4500 mL g(-1) h(-1), reaching the catalytic performance comparable to that of the optimal level of multifunctional catalyst operated at much higher pressure (6.0 MPa). This work highlights the potential of using MOF-derived quasi-MOF materials as a tunable platform to explore highly efficient catalysts for syngas conversion.
