
论文题目:Crystalline Multi-Metallic Compounds as Host Materials in Cathode for Lithium–Sulfur Batteries
论文作者:Yicheng Jiang, Hafiz Muhammad Umair Arshad, Haojie Li, Sheng Liu, Guoran Li*, Xueping Gao
Abstract:
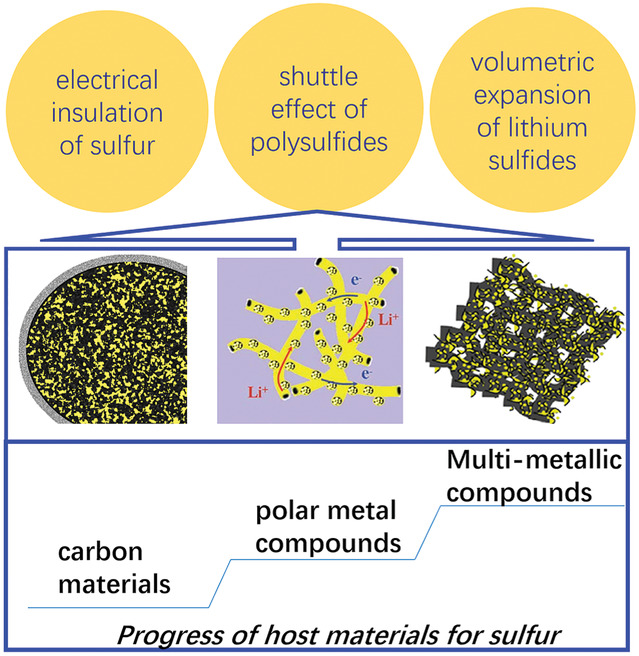
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery is one of the most promising next-generation rechargeable batteries. Lots of fundamental research has been done for the problems during cycling like capacity fading and columbic efficiency reducing owing to severe diffusion and migration of polysulfide intermediates. In the early stage, a wide variety of carbon materials are used as host materials for sulfur to enhance electrical conductivity and adsorb soluble polysulfides. Beyond carbon materials, metal based polar compounds are introduced as host materials for sulfur because of their strong catalytic activity and adsorption ability to suppress the shuttle effect. In addition, relatively high density of metal compounds is helpful for increasing volumetric energy density of Li-S batteries. This review focuses on crystalline multi-metal compounds as host materials in sulfur cathodes. The multi-metal compounds involve not only transition metal composite oxides with specific crystalline structures, binary metal chalcogenides, double or complex salts, but also the metal compounds doped or partially substituted by other metal ions. Generally, for the multi-metal compounds, microstructure and morphologies in micro-nano scale are very significant for mass transfer in electrodes; moreover, adsorption and catalytic ability for polysulfides make fast kinetics in the electrode processes.
